Back
Advanced Product Quality Planning ( APQP ) - Phases of APQP
Introduction to Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP):
Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) is a structured and comprehensive framework that plays a pivotal role in the automotive and other manufacturing industries. Developed as a collaborative effort between major automotive manufacturers and suppliers, APQP is now widely adopted across various sectors for its effectiveness in ensuring the delivery of high-quality products.
The primary goal of APQP is to proactively plan and manage all aspects of the product development process to meet or exceed customer expectations.
Key Components of APQP:
- Cross-Functional Team Collaboration:
- APQP emphasizes the formation of cross-functional teams involving representatives from various departments such as engineering, manufacturing, quality, and supply chain. This collaborative approach ensures that diverse perspectives are considered throughout the product development lifecycle.
- Phased Planning:
- APQP is organized into distinct phases, each with specific tasks and objectives. These phases typically include planning and definition, product design and development, process design and development, product and process validation, and finally, ongoing production.
- Risk Management:
- A crucial aspect of APQP is the identification and management of potential risks. This involves conducting thorough risk assessments to identify factors that could impact product quality, delivery, or cost. By addressing these risks early in the process, APQP aims to prevent issues during production.
- Quality Planning:
- APQP involves the creation of detailed quality plans that outline the critical characteristics of the product, customer requirements, and the quality control measures to be implemented. This ensures that quality standards are consistently met throughout the manufacturing process.
- Prototyping and Validation:
- Prototyping and validation are integral components of APQP. The process includes the development of prototypes for testing and validation purposes. This phase allows for the identification and correction of potential issues before full-scale production, contributing to the overall reliability of the final product.
- Continuous Improvement:
- APQP promotes a culture of continuous improvement. Feedback from each phase, including feedback from production and post-production phases, is used to refine processes and enhance product quality. This iterative approach ensures that lessons learned are applied to future projects.
Benefits of APQP:
- Reduced Defects and Rework:
- By proactively addressing potential issues, APQP helps minimize defects and the need for costly rework during production.
- Improved Time-to-Market:
- The structured approach of APQP contributes to efficient planning and execution, reducing the time it takes to bring a product to market.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction:
- APQP's focus on meeting customer requirements and expectations contributes to higher levels of customer satisfaction.
- Cost Savings:
- Through effective risk management and quality planning, APQP helps control costs associated with defects, rework, and production delays.
In conclusion, Advanced Product Quality Planning is a robust methodology designed to ensure that product development and manufacturing processes are well-planned, controlled, and capable of consistently delivering high-quality products. Its systematic approach, collaboration, and focus on continuous improvement make APQP a valuable tool for industries aiming to excel in quality and customer satisfaction.
What is APQP?
APQP, or Advanced Product Quality Planning, is your blueprint for exceptional product development.
Tailored for manufacturing excellence, APQP guides you through meticulous stages—from design to production—ensuring top-tier quality and customer satisfaction. Elevate your projects with this proactive approach, identifying and addressing potential issues with precision.
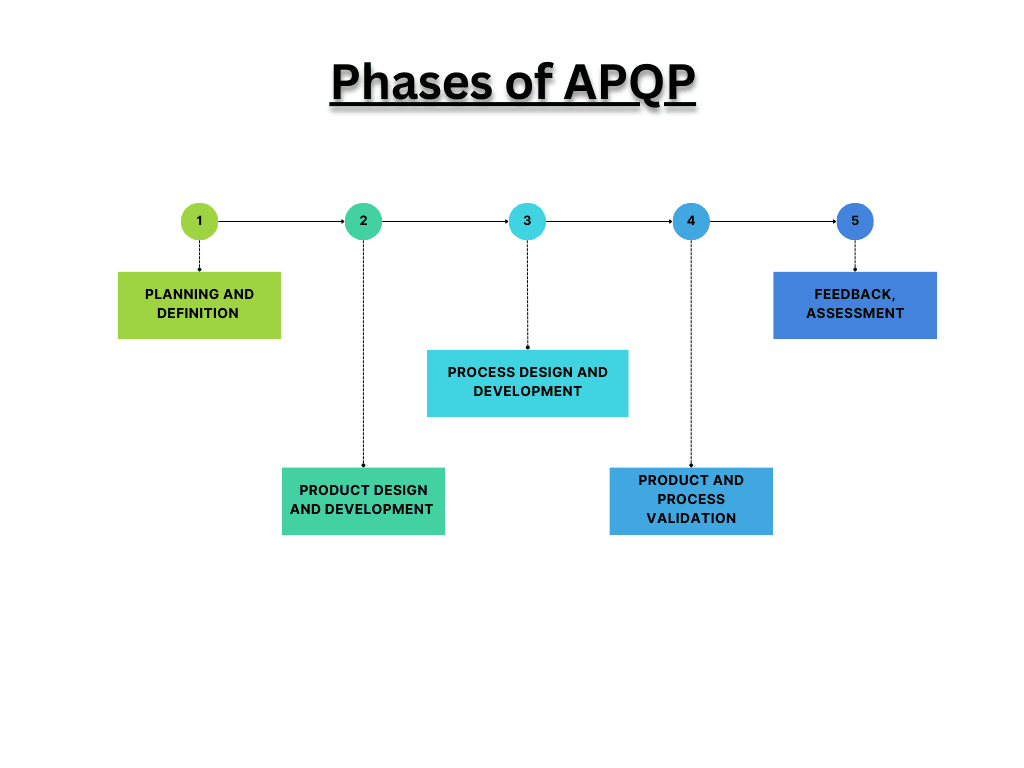
The 5 Phases of APQP
Phase 1: Planning and Definition
- Define the project scope, objectives, and requirements.
- Establish a cross-functional team.
- Conduct risk assessments and set initial project timelines.
Phase 2: Product Design and Development
- Develop product concepts and design specifications.
- Utilize tools like FMEA (Failure Modes and Effects Analysis) to assess potential risks.
- Create prototypes and validate the design.
Phase 3: Process Design and Development
- Develop and optimize the manufacturing process.
- Identify key process parameters and control plans.
- Conduct pilot runs to validate the production process.
Phase 4: Product and Process Validation
- Conduct comprehensive testing to validate the product and process.
- Verify that the product meets customer requirements.
- Ensure that the manufacturing process is capable of consistently producing quality products.
Phase 5: Feedback, Assessment, and Continuous Improvement
- Gather feedback from the production phase.
- Assess the overall performance of the product and process.
- Implement continuous improvement measures based on lessons learned.
These phases collectively ensure a systematic and quality-focused approach to product development, helping organizations deliver high-quality products to market.
History of APQP
Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) has its roots in the automotive industry and was initially developed by the Big Three American automakers: Ford, General Motors, and Chrysler (now Stellantis). The need for a systematic approach to quality planning arose as the automotive industry faced increasing global competition and a growing emphasis on quality management.
The history of APQP can be traced back to the late 1980s and early 1990s when the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG) was established. The AIAG is a not-for-profit association of automotive companies that collaboratively works to develop and promote common quality standards and practices in the automotive industry.
APQP was introduced as part of the AIAG's Quality Management System standards, particularly in the second edition of the QS-9000 standard, which was released in 1995. QS-9000 was a quality management system developed jointly by the Big Three automakers and was widely adopted in the automotive supply chain.
How is APQP related to PPAP?
APQP (Advanced Product Quality Planning) and PPAP (Production Part Approval Process) are two closely related elements within the automotive and manufacturing industries. Both are part of the quality management system and are often used in conjunction to ensure the production of high-quality products. Here's a brief overview of each and their relationship:
- APQP (Advanced Product Quality Planning):
- Focus: APQP is primarily focused on the early stages of product development and planning.
- Purpose: It aims to ensure that customer requirements are met by systematically planning and coordinating all activities during the product development process.
- Key Activities: APQP involves defining and documenting the project scope, identifying potential risks, developing quality plans, and establishing a cross-functional team to oversee the process.
- PPAP (Production Part Approval Process):
- Focus: PPAP, on the other hand, is more concentrated on the later stages of the product realization process, specifically during the production and pre-production phases.
- Purpose: PPAP is designed to demonstrate that the production process is capable of consistently producing parts that meet the specified requirements.
- Key Activities: PPAP includes the submission of sample parts, along with supporting documentation, to the customer for approval. This documentation demonstrates that the production process has been validated and is capable of meeting quality standards.
Relationship:
- APQP
- PPAP, as a part of the final stages of product realization, provides evidence that the production processes are in control and capable of producing parts that meet the established criteria, as outlined in the earlier APQP phases.
In summary, APQP is about planning and coordination in the early stages of product development, while PPAP focuses on providing evidence of process capability during production. Together, they contribute to a comprehensive quality management system, helping to ensure that high-quality products are consistently produced.



